Which Central Banks keep their gold in other countries and why?
Those Central Banks Which Keep Their Gold in Another Country
Many countries are concerned about the safe storage of their gold reserves. The main idea of the article is to see which Central Banks keep their gold reserves in other countries and why they are doing so.
In the first chapter, we will show that each country individually approaches the place of storage of its gold reserves.
In the second chapter, we will show that there is a trend in the countries of the European Union to repatriate their gold reserves.
In the third chapter, we will show that the USA and Great Britain are the largest custodians of foreign gold and consider the reasons for this.
1. Countries Make Different Approaches About the Place of Their Gold Storage.
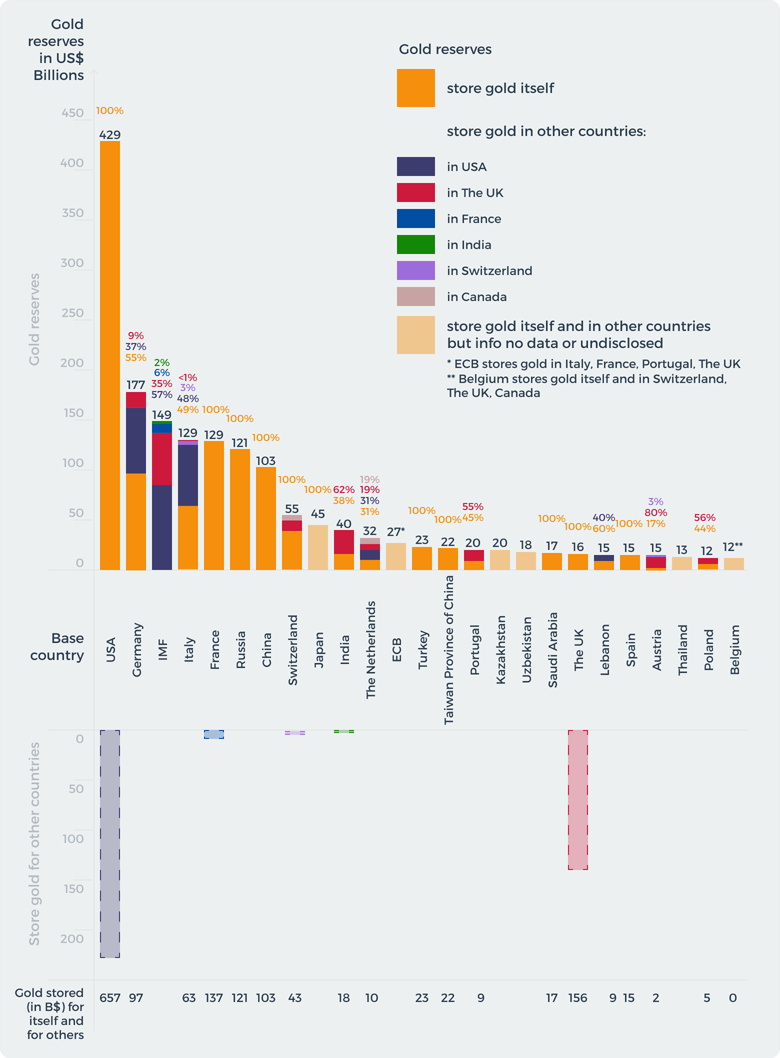
Safe and high-quality storage of their gold reserves is one of the most important tasks of the governments of countries. We considered 25 countries (including 2 institutions: the International Monetary Fund and the European Central Bank) that have the largest gold reserves.
We have identified 3 main groups of countries based on where their gold is stored.
The first group is countries that keep all their gold at home. These include the USA, France, Russia, China, Turkey, Taiwan, Saudi Arabia, Great Britain and Spain. The main characteristic of these countries is that they have enough space to store their own gold at home. The US has the largest gold reserve in the world. The world's largest gold depository, the Treasury by the U.S., is located in the United States Mint where the US keeps its 429 US$ billions gold reserves. Great Britain has the world's second largest gold vault in the Bank of England, so Great Britain keeps its 16 US$ Billions in the Bank of England.
According to the Banque de France all their gold in amount 129 US$ Billions is in the Bank's gold vaults are located in a set of chambers known as "La Souterraine" after they repatriated all their gold to home.
Russia and China have dramatically increased their gold reserves over the past decade and, according to their governments' policy, keep all their gold reserves at home. All Chinese gold is located in China in the People’s Bank of China. Although there is no official confirmation of gold storage arrangements, it is thought that the Chinese official gold reserves are vaulted in Beijing. These countries pursue their policies against the dominance of the dollar and try to diversify their assets. Another reason why Russia and China keep their gold at home may be the fear of putting a sanction on their assets. This storage is especially relevant for Russia after the freezing of the assets of their Central Bank of Russia by Western countries.
The second group of countries are countries that keep their gold abroad. These include Germany, Italy, Switzerland, India, the Netherlands, Portugal, Libya, Austria, Poland and Belgium. These countries are characterized by the fact that they do not have enough space to store gold at home, and also due to historical or political reasons, part of their gold reserves are stored abroad. For example, Germany keeps 80 billion of its gold reserves abroad, mostly in the USA. This decision is due to the fact that after the Second World War there were fears that the Soviet Union could steal Germany's gold reserves, and West Germany was an ally of the United States, so they decided to move their gold to a safe storage bowl. Italy also keeps 67 billion of their gold reserves abroad, mostly in the US, which is 51% of their reserves.
Some countries have problems with the quantity and security of placing all their gold reserves in their country, so they store their gold abroad. For example, Belgium and India, which do not have enough money to store their gold at home, store their gold in Great Britain and Canada. Or Lebanon that keeps its gold in France.
And the third group of countries are countries that do not publish the place of storage of their gold reserves. These include Japan, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan and Thailand. Sometimes countries or institutes do not want to publish information about the storage location and amount of gold due to certain reasons that influence the government's decision. For example, Belgium and the European Central Bank publish only where they store gold, but not the amount. There are countries like Japan or Thailand that do not publish any information regarding the storage of their own gold.
2. European Union Countries Repatriate Their Gold
Gold repatriation refers to the government's plans to bring home gold reserves stored abroad. In 2013-2014, the central banks of Germany, France, the Netherlands, Belgium and Austria announced their desire to return their gold home.
In January 2013, the Deutsche Bundesbank, Germany's central bank, announced plans to repatriate 300 tons (16.8 US$ Billions) of its reserve from the United States and 374 tons (21 US$ Billions) from France by 2020 to store 1847 tons (103.7 US$ Billions) its official gold reserves in Frankfurt. The gold held in the US was purchased by West Germany during the period of active trade surplus with the US until 1970. The gold was never returned to Germany due to fears of a Soviet invasion. In 2016, Germany completed the repatriation of gold home.
In 2014, De Nederlandsche Bank said it "believed that during a financial crisis it is better to have gold on hand." The Netherlands returned 122.5 tons (6.8 US$ Billions) of gold reserves from the USA.
In 2013, during the LBMA conference in London, the Director of Market Operations of the Bank of France, Alexandre Gautier, announced plans to return French gold home. In 2014, the leader of the French Nationalist Party, Marine Le Pen, wrote an open letter to Christian Noyer, governor of the Banque de France, demanding to start the repatriation of French gold home. The central bank of France has covertly repatriated 221 tons (11.65 US$ Billions) of gold between 2013 and 2016. Today, France keeps all its gold reserves at home.
Belgium and Austria have also announced plans to repatriate their gold, but the repatriation process is still ongoing. Austria plans to keep 50% of their gold reserve (7.5 US$ Billions) at home. Poland, Romania and other countries also joined them in a process of gold repatriation.
3. The USA and Great Britain are the Largest Custodians of Foreign Gold
The graph below shows that the United States and Great Britain together store more than 812 US$ Billions gold, which is 53% of all the world's gold reserves. In total, the 5 largest countries store more than 75% of all the world's gold in their gold vaults.
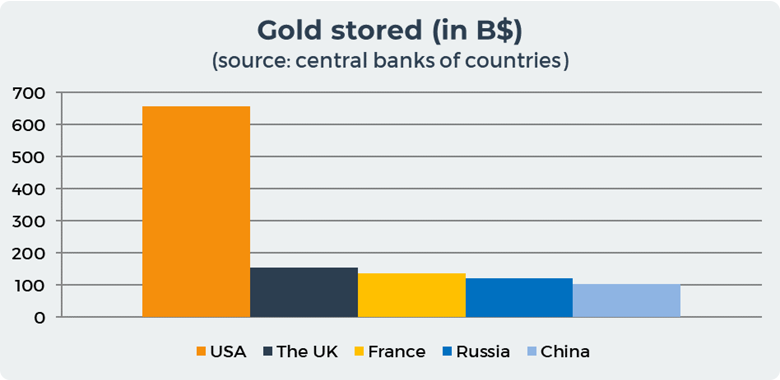
In the USA, the largest repository of gold in the world is The United States Mint, which is a bureau of the Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bullion. They own 4 gold vaults in Philadelphia, Denver, San Francisco, and West Point. Almost all gold in the United States is stored in Fort Knox. Its primary purpose is for storage of the United States and other countries' gold and silver bullion reserves. In total, the USA keeps 657 US$ Billions or 43% gold of the 25 countries with the largest gold reserves.
3b. Why Do Countries Keep Their Gold in the US and UK?
The main reason for storing gold in the US and UK is for security reasons and historical reasons. A lot of gold was moved during World War 2 to avoid theft of gold reserves. Governments decide to place their gold in a network of different banks to make sure their gold is safe. For example, according to the Bank of England reports, there has not been a single theft of gold in over 150 years.
The second reason is insufficient facilities for storing gold. Not all countries have sufficient facilities for safe storage of large amounts of gold. Transporting gold is a very expensive operation, so countries store their gold where they buy it. Transporting and moving gold is also a risky operation. Therefore, most countries simply ask other governments to transfer ownership of some of their gold reserves to them, keeping the physical reserves in their country.
London and New York are centers (there are also others) for gold trading and the banks save money by buying the gold on, say, the London market, leaving it in London, then selling it to, say, Japan in the London market and not transporting it around the globe. There is also a practice of lending out gold and being repaid in gold and the interest is also paid in a specific agreed amount of gold.
Conclusion
Each country decides for itself where and how to store its gold reserves. Some decides to keep them in their country, some keeps their gold abroad due to political, security or lack of opportunities to store gold. However, we have seen that the policy of nationalism has intensified, which has caused a chain reaction to the return of gold to the EU countries. New developing countries are also appearing on the gold market and are actively increasing their gold reserves by diversifying their assets and pursuing a policy against the dominance of gold. We see that London and New York continue to play an important role in the storage and trade of gold in the world, and that they are among the most reliable and safest places to store gold, according to which many countries continue to store their gold in the USA and Great Britain.
Date= 3rd February 2023, Gold price – 1925.50$, Silver price – 23.71$, Platinum price – 1047.50$, Oil price – 75.83$